Over the years millions of dollars have been spent on extensive studies to determine what factors influence the adoption of new technology. With billions of dollars at stake, it's no wonder why. This article attempts to boil down the findings of these studies into practical information that organizations can use to optimize the adoption of their digital channel, also known as their Web site.
The adoption of new technology by people comes down to changing behavior: getting people to do something a new way or to do something that they have been unable to do before. As such, we must first understand the factors that cause us humans -- not always graceful with change -- to see enough value to warrant a change in our behavior.
Although the studies have focused on several different factors that can influence a consumer’s willingness to adopt new technology, three primary factors have been consistently found to have a direct impact:
-
The perceived risk of using the technology.
-
The perceived value of the technology.
-
The technology’s perceived ease of use.
|
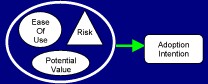 |
As expected, these factors are directly related to one another. For example: the greater the perceived risk, the greater the perceived value and/or the easier the technology must be to use to warrant a consumer to adopt the technology. Since we are talking about perceptions here, which may or may not be based on facts, the psychological makeup of the consumer must be taken into account to get a better sense for how these factors may impact each other.
Several studies have broken down consumers into 5 distinct groups: Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority and Laggards. "Innovators" and "Early Adopters" are the first two groups to adopt new technology and represent approximately 15% to 21% of the US population. These two groups of con
Two of the primary risk factors perceived by consumers include the risk of financial loss and the risk of lost privacy. Neither of these perceived risks can be entirely eliminated – especially for consumers that have a high degree of risk aversion -- but ensuring that consumers are fully educated as to the actual risks involved can certainly mitigate these perceived risks. Perceptions of potential financial loss are best addressed by providing information in simple terms that defines how consumers are protected against financial loss along with pointing to the lack of financial breaches in your digital channel.Issues with privacy concerns take two forms that must both be addressed:
1. You must ensure that your Privacy Policy is readily available and states in understandable and certain terms that their information will not be shared with anyone outside your organization.
2. You must provide your consumers with a method to opt-out of receiving any promotional information not specifically signed up for.
Innovators" have a high tolerance for risk when adopting new technology and do not necessarily need to see much immediate value for them to dive into new technology headfirst. Some also say that these early adopters of technology understand the risk for what it is and see the true potential of technology before others. I think it is probably a combination of both these lines of thought!
The other groups, representing 75% to 85% of the US population, are more risk averse and require more validation that it is worth assuming the perceived risk before adopting the new technology.
Perceived Value and Ease of Use
Consumer perceptions of the value and ease of use of your digital channel clearly can and should be molded through education and marketing efforts. However, for most consumers, education and marketing alone is unlikely to overcome the perceived risks of online banking services when compared to the associated perceived value and ease of use.
Consumers are looking for a migration path that allows them to get comfortable with your digital channel using things they consider to be less risky and easier to use before jumping into the "deep end of the pool" with online banking services. Once consumers get more comfortable with the "shallow end" of your digital channel, they are more apt to venture into deeper waters and begin using your online banking services.
An effective method for providing your consumers with a migration path to your online banking services is to promote your digital channel as an alternative support channel. By getting your consumers to begin using your digital channel to research your products, services and related personal finance information, and then by allowing them to escalate to a real person if they need additional help, you are providing them with a migration path that allows them to get comfortable with your digital channel using things they are already comfortable with: email and research. In addition, your digital channel also provides an excellent opportunity to educate and market to your consumers about all of your online services.
Conclusion
Human behavior is unique to each individual but common factors exists for all consumers when determining their likelihood of adopting new technology. Some consumers are quick to embrace new technology but the vast majority of consumers need to see clear value for them to assume the perceived risk and time required to learn and use new technologies.
Organizations can expedite this natural technology adoption process by providing consumers with a migration path that allows them to get comfortable with new technology at their pace. By making their digital channel a viable alternative support channel to in-person and phone support, organizations can effectively address known behavioral factors impeding the adoption of their digital channel.